Question 1:
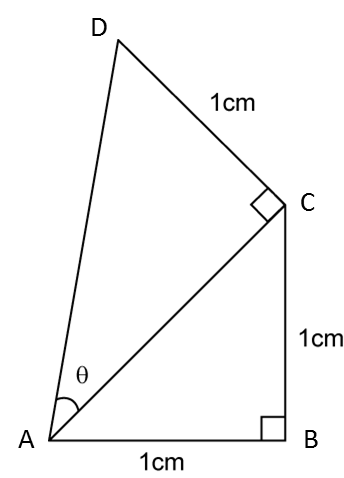
In the diagram above, find the value of tan θ.
Solution:

In the diagram above, find the value of tan θ.
Solution:
Question 2:
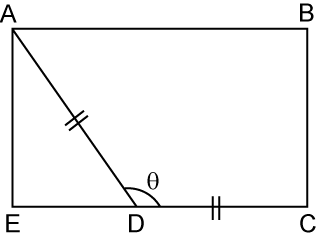
In the diagram above, ABCE is a rectangle and point D lies on the straight line EC. Given that DC = 5 cm and AE = 4cm, find the value of cosθ.
Solution:

In the diagram above, ABCE is a rectangle and point D lies on the straight line EC. Given that DC = 5 cm and AE = 4cm, find the value of cosθ.
Solution:
Question 3:
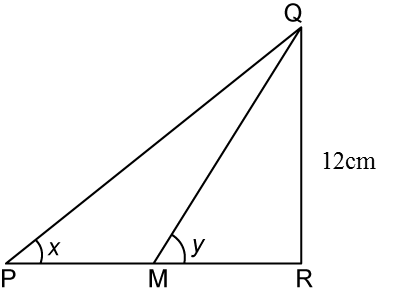
In the diagram above, PMR is a straight line, M is the midpoint of line PR. Given that QR = 12cm and sin y°= 0.6, find the value of tan x°.
Solution:

In the diagram above, PMR is a straight line, M is the midpoint of line PR. Given that QR = 12cm and sin y°= 0.6, find the value of tan x°.
Solution: