Question 1:
Solution:
(a)
(b)

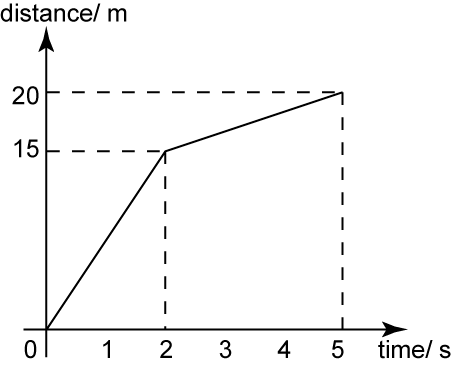
The diagram above shows the distance-time graph of a moving particle for 5 seconds. Find
(a) the distance travel by the particle from the time 2 second to 5 second.
(b) the speed of the particle for the first 2 seconds.
Solution:
(a)
Distance travel by the particle from the time 2 second to 5 second
= 20 – 15
= 5 m
(b)
The speed of the particle for the first 2 seconds
= Gradient
Question 2:
Solution:
(a)
(b)

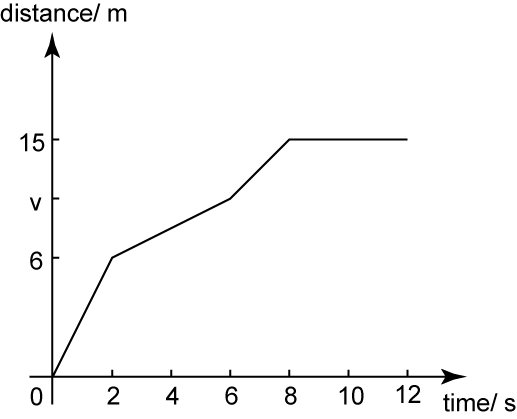
The diagram above shows the distance-time graph of a moving car for 12 seconds. Find
(a) the value of v, if the average speed of the car for the first 6 seconds is 2 ms-1.
(b) average speed of the car for the first 8 seconds.
Solution:
(a)
(b)
Question 3:
Diagram below shows the distance-time graph for the journey of a train from one town to another for a period of 90 minutes.

(a) State the duration of time, in minutes, during which the train is stationery.
(b) Calculate the speed, in km h-1, of the train in the first 40 minutes.
(c) Find the distance, in km, travelled by the train for the last 25 minutes.
Solution:
(a) Duration the train is stationery = 65 – 40 = 25 minutes
(c) 90 – 0 = 90 km
Diagram below shows the distance-time graph for the journey of a train from one town to another for a period of 90 minutes.

(a) State the duration of time, in minutes, during which the train is stationery.
(b) Calculate the speed, in km h-1, of the train in the first 40 minutes.
(c) Find the distance, in km, travelled by the train for the last 25 minutes.
Solution:
(a) Duration the train is stationery = 65 – 40 = 25 minutes
(c) 90 – 0 = 90 km
Want more activities in this chapter
Thank you!!