4.3a Intersection of Sets
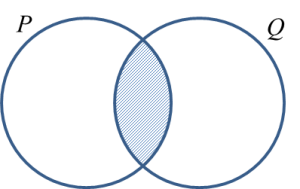
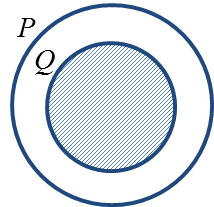
1. The intersection of set P and set Q, denoted by
is the set consisting of all elements common to set P and set Q.
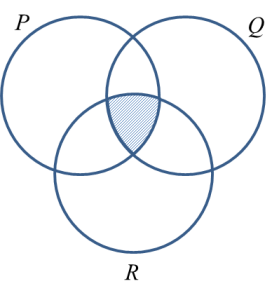
2. The intersection of set P, set Q and set R, denoted by is the set consisting of all elements common to set P, set Q and set R.
3. Represent the intersection of sets using Venn diagrams.
(a) P ∩ Q

(d) P ∩ Q ∩ R
Example 1:
Given that A= {3, 4, 5, 6, 7}, B = {4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 12} and C = {3, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10}.
(a) Find A∩B∩C.
(b) Draw a Venn diagram to represent A∩B∩C.
Solution:
(a) A∩B∩C= {5, 7}
(b)
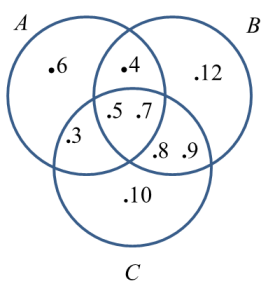
(b)

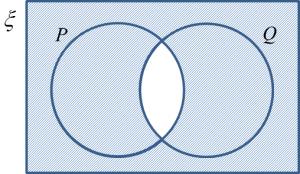
4. The complement of the intersection of two sets, P and Q, represented by (P ∩ Q)’, is a set that consists of all the elements of the universal set, ξ, but not the elements of P ∩ Q.
5. The complement of set (P ∩ Q)’ is represented by the shaded region as shown in the Venn diagram.